How it all started
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a subfield of artificial intelligence (AI) focused on enabling computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language in a meaningful way. Spanning over seven decades, the development of NLP has been marked by foundational breakthroughs, paradigm shifts, and increasingly sophisticated models.
Early Beginnings: The 1950s — 1980s
The roots of NLP trace back to the 1950s, when pioneers like Alan Turing introduced foundational ideas such as the Turing Test to evaluate machine intelligence. Early approaches were largely rule-based and grounded in linguistic theories.
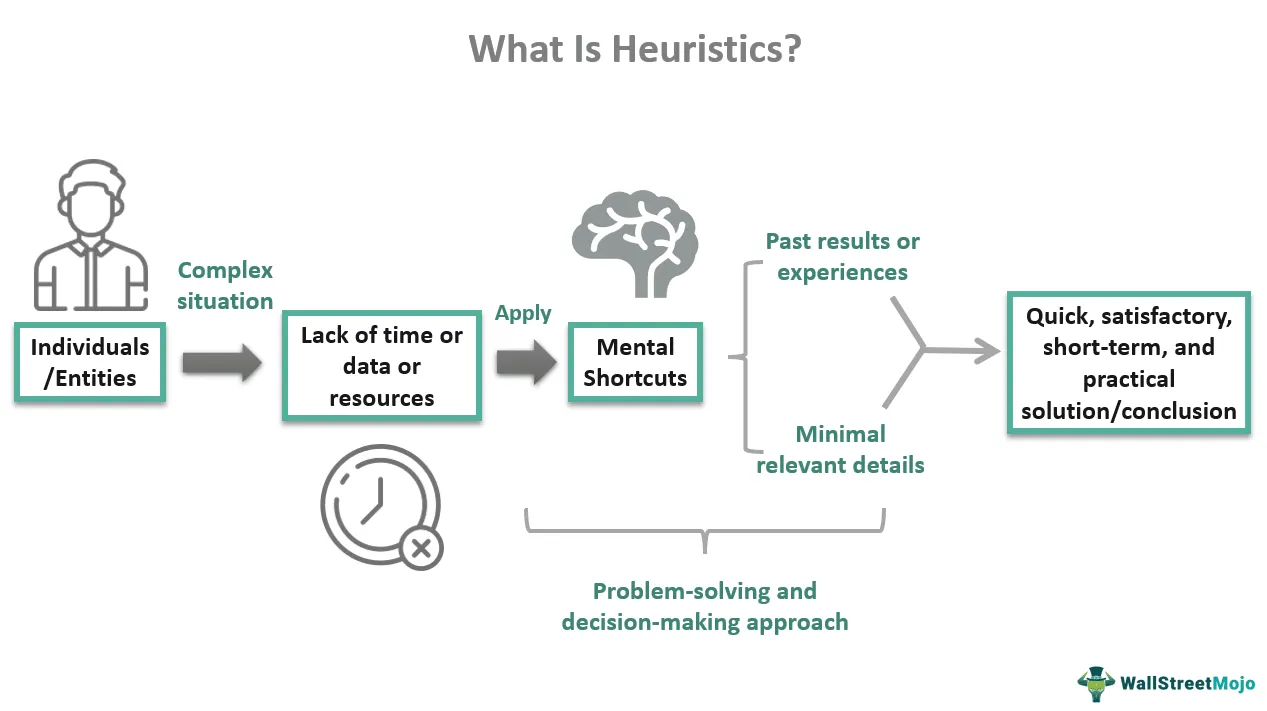
Heuristic-Based Methods
- Regular Expressions: Used for basic pattern matching tasks (e.g., dates, emails).
- WordNet: A lexical database organizing words into synonym sets (synsets), capturing semantic relationships.
- Open Mind Common Sense: A crowd-sourced initiative to build a commonsense knowledge base for machines.
The Statistical Era: 1990s
With the rise of computational power and access to large corpora, the 1990s saw a shift to statistical NLP, using probabilistic techniques to handle ambiguity and language variability.
Statistical & Machine Learning Methods
- Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) and n-gram models for speech tagging and recognition.
- Decision Trees, Naive Bayes, and SVMs for classification.
- Heavy reliance on feature engineering to transform text into numerical formats.
Text Vectorization Techniques
- Bag of Words (BoW): Frequency-based representation.
- TF-IDF: Highlights important words by weighing term frequency against document frequency.
- Word Embeddings: Semantic vector representations (e.g., Word2Vec, GloVe).
The Deep Learning Revolution: 2010s
The 2010s brought a breakthrough with deep learning, allowing models to learn directly from raw data with minimal feature engineering.
Neural Architectures
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): Good for sequences but suffer from vanishing gradients.
- LSTMs and GRUs: Address long-term dependencies.
- CNNs: Capture local and hierarchical patterns.
Transformers & Language Models
- BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers): Contextual embeddings from both directions.
- GPT (Generative Pretrained Transformers): Focuses on coherent and context-aware text generation.
Autoencoder Models
- Encoder-Decoder Architectures: Encode input sequences into latent spaces and reconstruct output — key for translation and summarization tasks.
Modern NLP: 2020s and Beyond
Today, NLP continues to advance rapidly, supported by larger datasets, better hardware, and innovative techniques.
Key Trends
- Large Pretrained Models: Like GPT-3, BERT, LLaMA, Gemini, Claude, etc.
- Transfer Learning: Fine-tuning large models for domain-specific tasks.
- Multimodal Learning: Combining text with vision/audio for richer understanding.
- Ethics & Explainability: Ensuring fairness, mitigating bias, and improving model interpretability.
Conclusion
From symbolic logic to deep neural networks, NLP’s evolution mirrors the broader development of AI. Its techniques now power chatbots, translators, search engines, and virtual assistants used by millions daily. With future innovations like multilingual alignment, zero-shot reasoning, and multimodal cognition, NLP stands as a cornerstone of modern intelligent systems.
Written by Lavish Gangwani
AI Engineer | AI Researcher | Data Scientist
Medium
LinkedIn
GitHub
